Corneal Transplant
The cornea is the transparent, dome-shaped window covering the front of the eye. It is a powerful refracting surface, providing 2/3 of the eye's focusing power. There are no blood vessels in the cornea, it is normally clear and has a shiny surface. The cornea is extremely sensitive - there are more nerve endings in the cornea than anywhere else in the body.
Symptoms of Corneal Disease
People with cataract, even when wearing glasses, typically experience:
Pain
Blurred vision
Tearing
Redness
Extreme sensitivity to light
Types of Corneal Disease
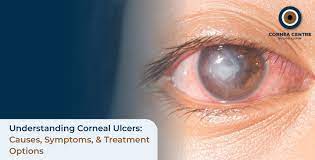
Corneal Ulcer (Keratitis). A sore on the cornea of the eye.The cornea is the clear layer at the front of the eyeball that has a protective function. The ulcer can have bacterial or viral origins or can result from injury to the cornea. The condition may range from severely painful to mildly irritating depending on the origin.
Corneal flash burns. An injury to the cornea caused by bright lights. The cornea is the clear layer at the front of the eyeball that has a protective function. Exposure to UV radiation from the sun, welder's arc or sun lamps can all result in corneal flash burns.
Corneal injury. A scratch, cut or minor injury on the cornea. The cornea is the clear layer at the front of the eyeball that has a protective function. The cornea can be injured by such things as dirt or sand getting in the eye or even vigorous rubbing of the eye. Corneal abrasions may be very painful and can cause symptoms such as tearing, blurred vision and headaches, full thickness corneal thickness may need surgical involvement.
Corneal foreign body is one of the common out - patient emergency which can be normally removed with a slit lamp.
Corneal Dystrophies & Degeneration. Corneal dystrophy is a condition in which one or more parts of the cornea lose their normal clarity due to a buildup of cloudy material. There are over 20 corneal dystrophies that affect all parts of the cornea.
Keratoconus. This disorder is a progressive thinning of the cornea. It is more prevalent in teenagers and adults in their 20s. Keratoconus arises when the middle of the cornea thins and gradually bulges outward, forming a rounded cone shape. This abnormal curvature changes the cornea's refractive power, producing moderate to severe distortion (astigmatism) and blurriness (nearsightedness) of vision. Keratoconus may also cause swelling and a sight-impairing scarring of the tissue.
A noninflammatory, usually bilateral protrusion of the cornea, the apex being displaced downward and nasally. It occurs most commonly in females at about puberty. The cause is unknown but hereditary factors may play a role. The -conus refers to the cone shape of the corneal protrusion.
Hyphema.
Bleeding between cornea and iris.
Trachoma is a chronic follicular conjunctivitis that leads to scarring in the conjunctiva and cornea. Repeat active infections occur in children < 10 years of age. Subsequently, conjunctival scarring (cicatricial disease) and inversion of the eyelashes so they irritate the cornea (trichiasis) develops as a result of earlier infections. Trichiasis predisposes to corneal ulceration and corneal opacities resulting in decreased vision and blindness.
Treatment of Corneal Disorders
Amniotic membrane transplantation
Botulinum toxin-A induced ptosis
Conjunctival/Corneal biopsy
Conjunctival flap - Gunderson's
Conjunctival flap - pedicle
Corneal biopsy
Corneal micropuncture
Corneal scraping
Corneal transplantation
Lamellar Keratoplasty
Penetrating Keratoplasty
DLK
DSAEK
Pterygium excision and conjunctival graft
Removal of a calcified band keratopathy
